Shopping Cart
-
 Autem ipsa ad 1 x $145.80
Autem ipsa ad 1 x $145.80 -
 Tenetur illum amet 1 x $150.80
Tenetur illum amet 1 x $150.80 -
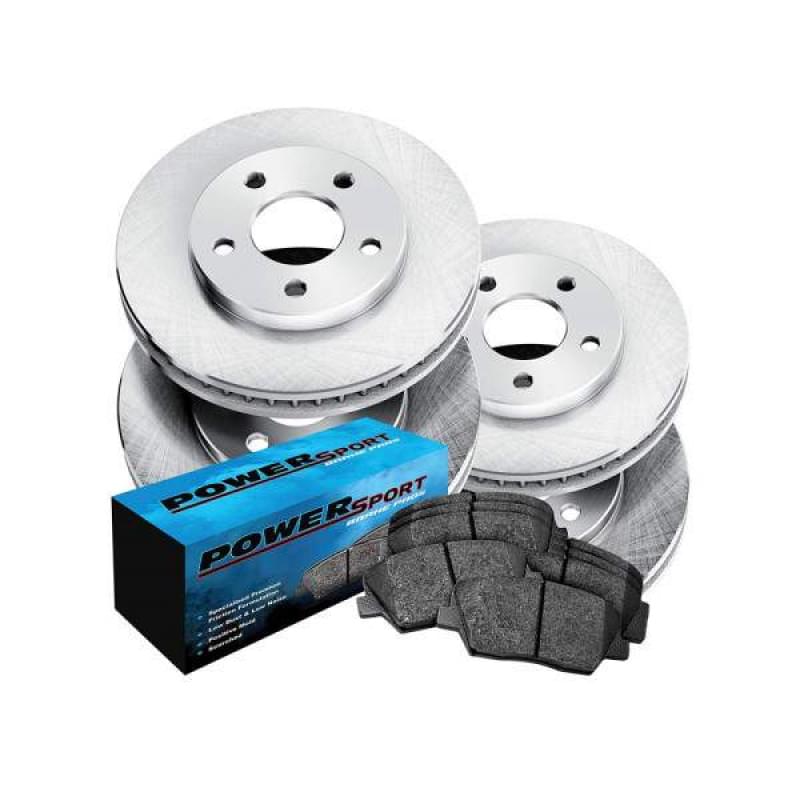
 Non doloremque placeat 1 x $165.80
Non doloremque placeat 1 x $165.80



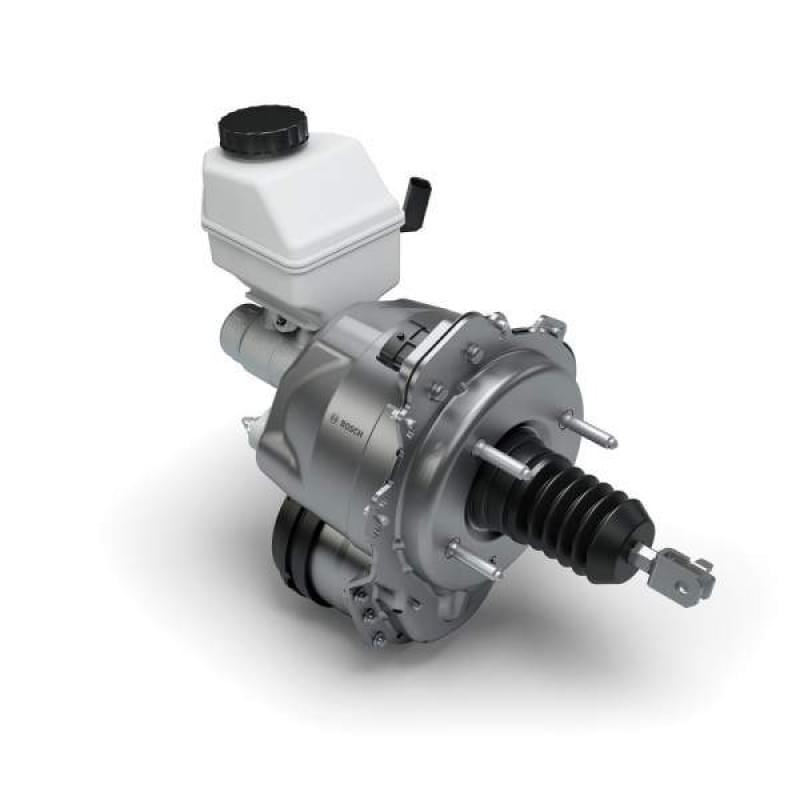
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
The invention relates to an electromechanical brake booster with an electric motor and a helical gearing. The brake booster is used for coupling an auxiliary force via a driver into a piston rod. The invention proposes connecting a spindle of the helical gearing elastically via a spring element to the piston rod such that, in the event of rapid actuation of the brake, the helical gearing and a rotor of the electric motor do not have to be accelerated entirely muscle power. The muscle power required for actuating a brake is reduced as a result in the event of a rapid actuation of the brake.
Get E-mail updates about our latest shop and special offers.
We are a team of designers and developers that create high quality HTML Template & Woocommerce, Shopify Theme.
Weiler Web Services All Right Reserved.